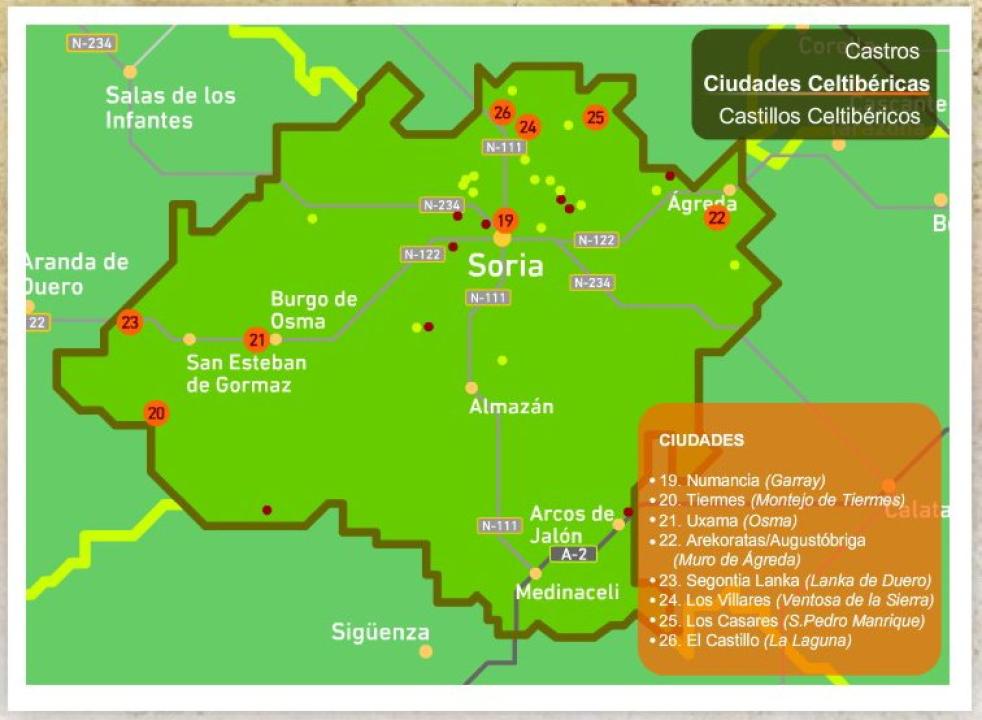

During the third century BCE is consolidated in the Upper Douro, agricultural economic orientation, embodied in rural settlements of mixed economy, with an increase in the intensification of trade and commerce. This was articulated with the internal evolution of its institutions, will crystallize before the Roman conquest in the creation of cities, which would enable the development of handicraft and services that make the difference between country and city, incorporating writing, using the Iberian signario to translate their Celtic language, and coinage, and Roman under concession.
Celtiberian world organization upon arrival in Rome was of city-states, such as organizing centers, administrative and political territories, where there are villages and towns. The importance of cities is reflected in the fact that they are the ones who deal directly with Rome, being received independently and those who sign agreements