The Roman impact on settlements began to acknowledge especially during the first century BC In a century was modified greatly Celtiberia, using the city as an instrument of Romanization and territorial control center, which led to a strong and standardized approach to building complex in the urban and monumental buildings as well as dissemination and uniformity many aspects of material culture, to transmit the ideology of Roman imperial power.
Some cities Celtiberian Soria province interrupted their occupation for a while, probably Numancia after its conquest in 133 BC, to be recovered from Augustus Arekorataz from the early first century BC, for relaunched with a new name: Augustobriga, which also refers to the same period. On the other hand, Termes who participated, with other cities, in a revolt against Rome in 98 BC, was conquered by Titus Didius, and forced to move to the lower, showing its continuity for the burials of the cemetery. Uxama, which was very active in Sertoriana Wars (80-72 BC), being burned by Pompey, shows the continuity of the data provided by its necropolis. Finally, Segontia Lanka correspond to a late foundation.
Concern about water supply in large complex concrete tanks and pipelines, as in Tiermes and Uxama. The adoption of the Roman house model, such as plinths in Uxama and the aqueduct in Tiermes reflects the adoption of the new lifestyle of the new ruling classes. (tanks and aqueduct Uxama Tiermes)
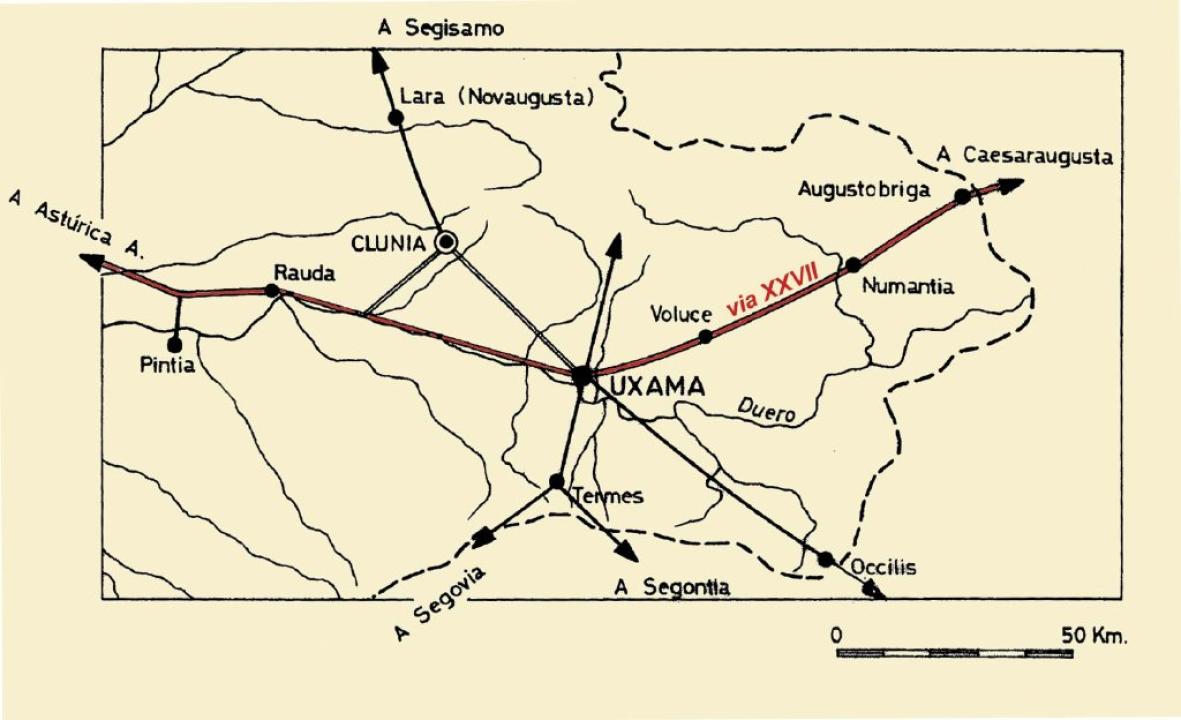
He also received major boost trade in goods and movement of people, brought about by two main Roman roads and other secondary crossing the area, especially that linked Caesaraugusta (Zaragoza) with Asturica (Astorga), through the Douro Valley, and another by the Jalon Valley since Caesarauguata came to Emerita Augusta (Merida). These are (with the Roman roads map)
However, funeral inscriptions show the survival of indigenous and other groups suprafamiliares stelae, decorated with the figure of the rider, reflect the effect of a full iconographic type of connotations, such as those found in Borobia.